Prepare for Wildfire Season: Protecting Your Health Amidst Poor Air Quality
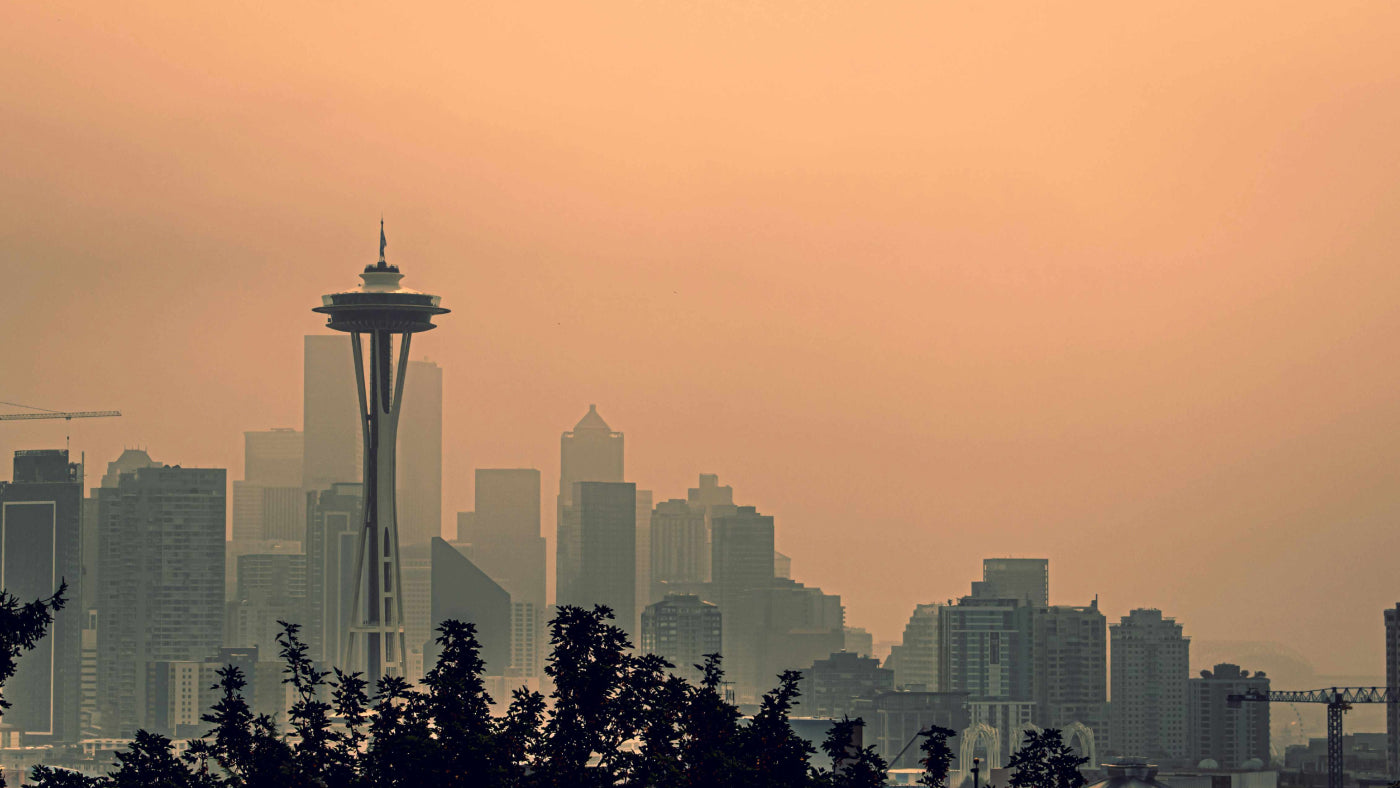
As the wildfire season begins, it's important to stay alert to the changes in air quality, not just for those close to wildfires but those in urban areas too. Recent incidents have shown that wildf...
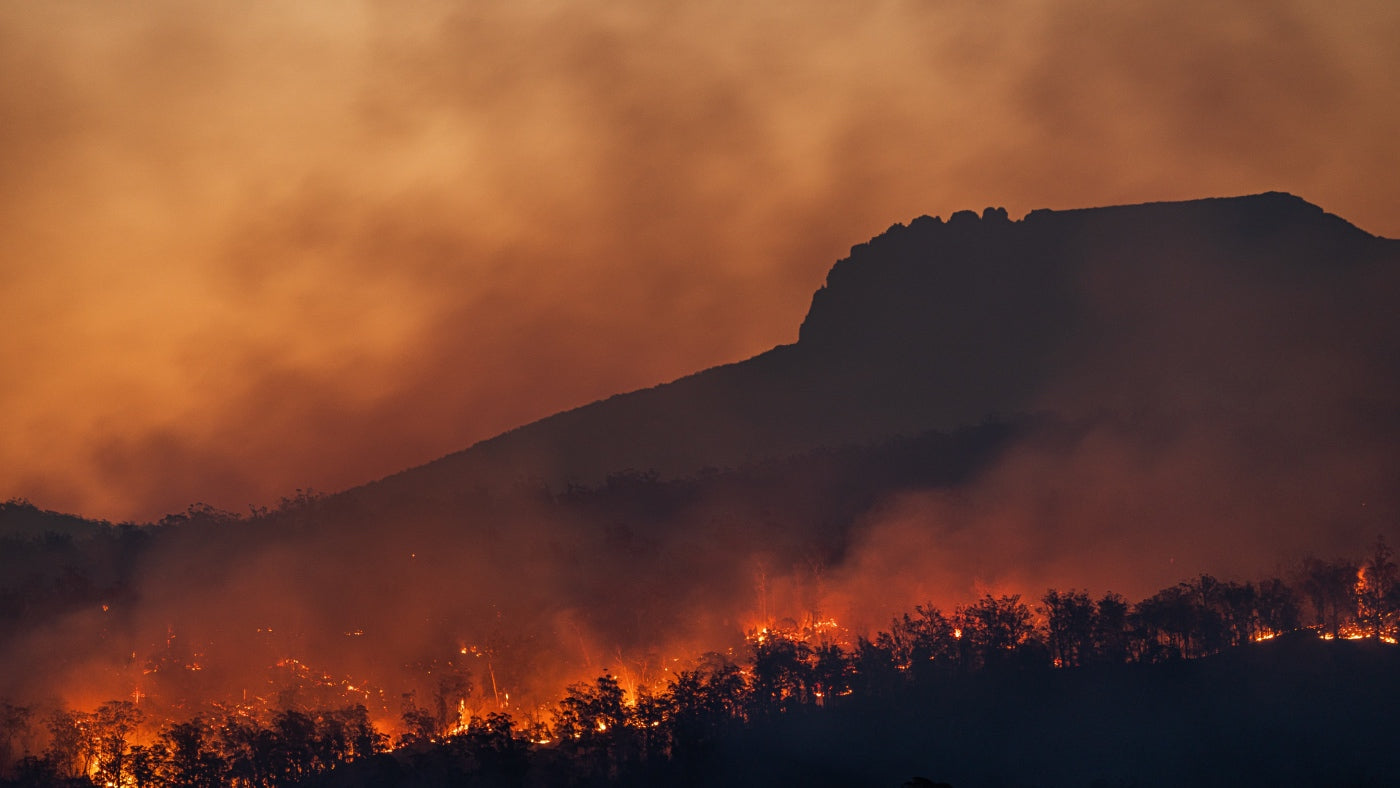

The Impact of Bushfires on Air Quality
The health toll of wildfire smoke extends far beyond the immediate vicinity of the blazes, with a staggering estimated global count of 340,000 premature deaths annually—surpassing the direct casual...
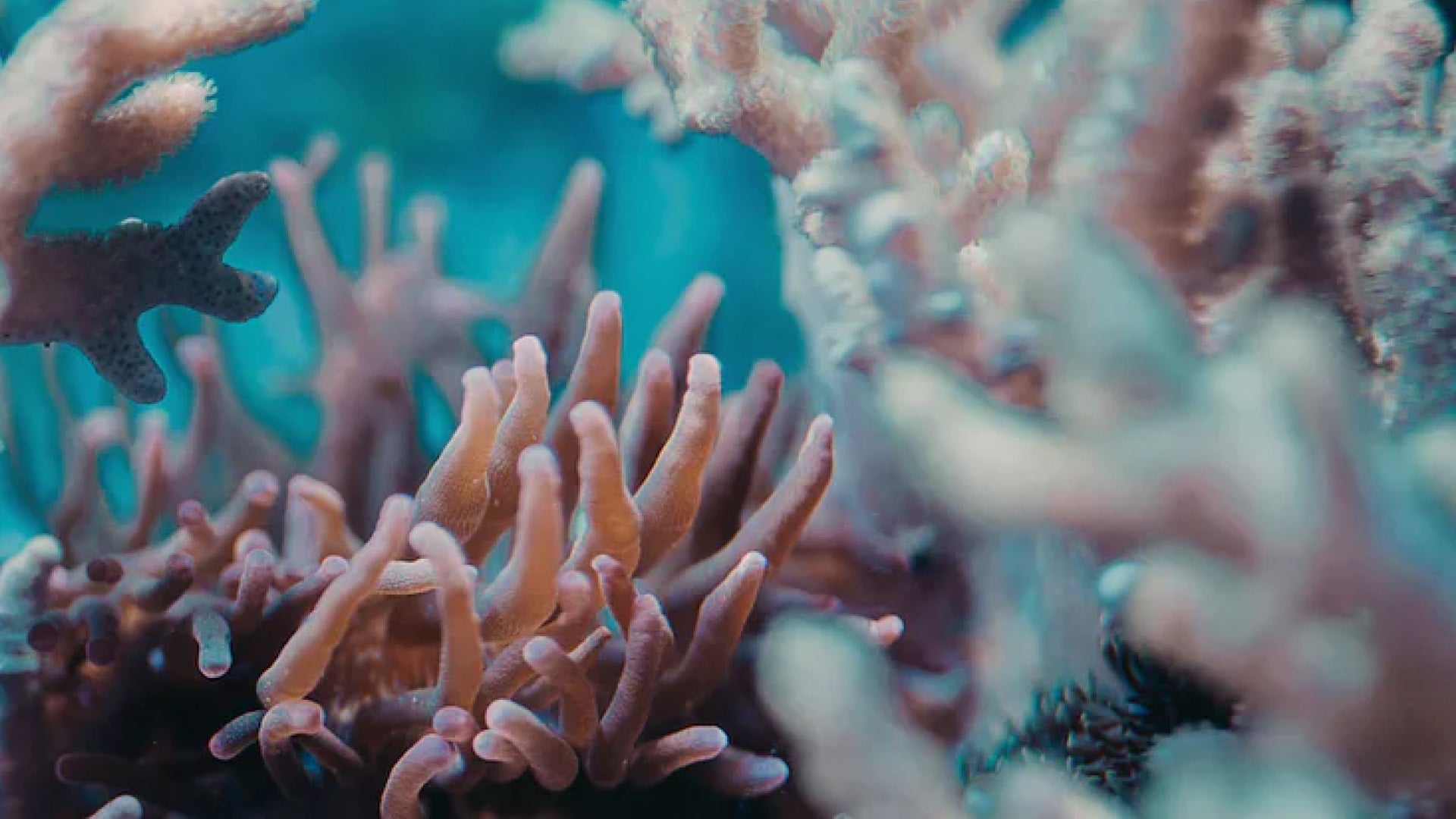

Delivering New Life to the Great Barrier Reef
As part of our ongoing effort to be a company that positively impacts the planet and the people on it we have partnered with The Great Barrier Reef Foundation for the launch of our Climate Blue Mas...
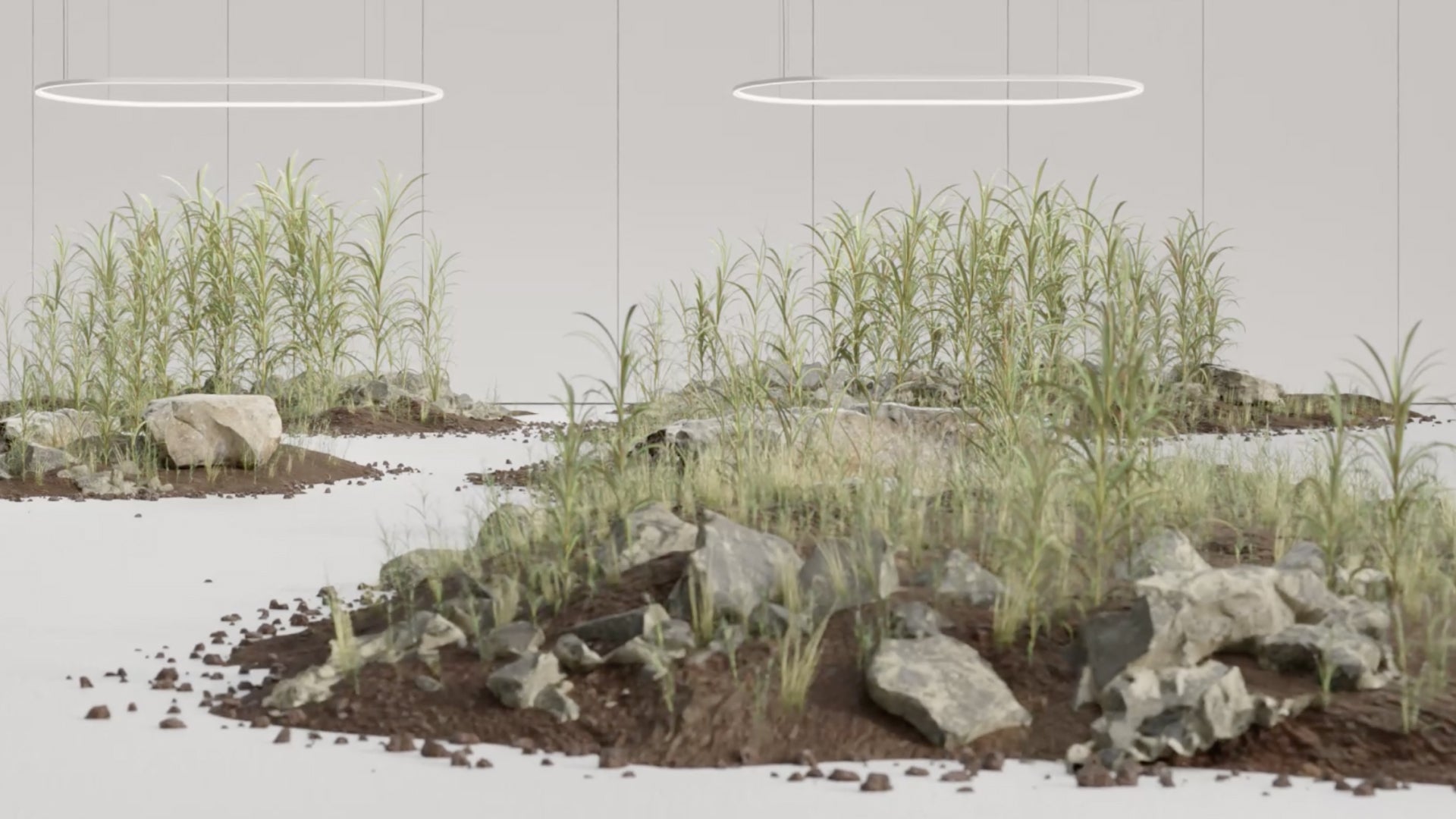

Sugarcane, The Sustainable Polymer
Sugarcane production has a much lower carbon footprint when compared to traditional petrochemical polymers. This is thanks to its ability to sequester carbon during growing, requiring less energy a...

Protecting Yourself From Air Pollution: Face Masks with Filters
Air pollution is a serious problem that affects people all over the world. It is a mixture of natural and man-made substances in the air that can be harmful to human health and the environment. The...